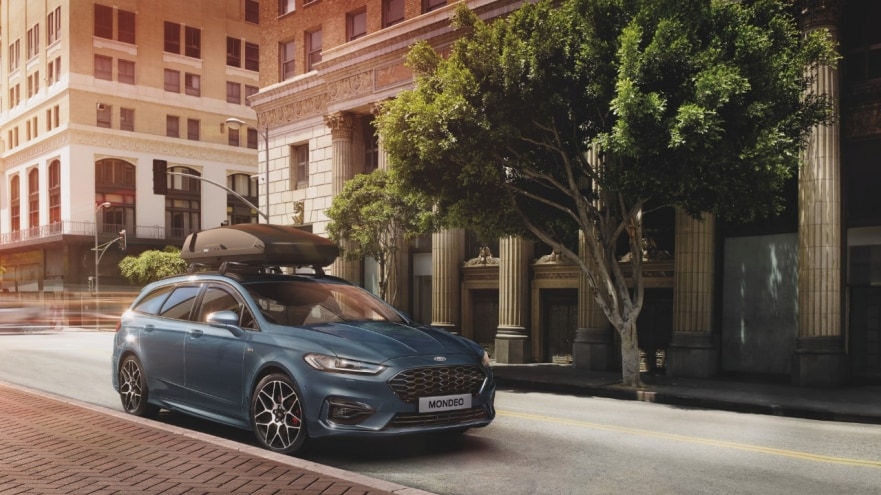
Ford has switched 100 per cent of petrol engine Mondeo production to full hybrid powertrains, the company announced today.
The Mondeo Hybrid delivers pure-electric driving capability without the need for customers to use an external power source to charge the battery. Full hybrid powertrain technology is among the solutions helping Ford customers transition to electrification with confidence, and can be particularly beneficial for drivers desiring increased refinement and fuel efficiency, but lacking access to an external charge point at home or work.
Mondeo Hybrid increased its share of total Mondeo sales by 25 per cent in Europe during the first seven months of this year compared with full-year 2019, to account for more than one third of all Mondeo sales.
By the same measure, Mondeo Hybrid grew in popularity by more than 50 per cent in the UK, and by more than 40 per cent in Italy, where 75 per cent of Mondeo customers chose the Mondeo Hybrid during the first seven months of 2020.
Ford last year expanded the Mondeo Hybrid line-up to include a first-in-segment wagon model and Mondeo Hybrid ST-Line variants with sporty styling inspired by Ford Performance, in addition to stylish Titanium and upscale Vignale versions. Mondeo four‑door and wagon customers will now have the choice of fuel-efficient full hybrid or 2.0‑litre EcoBlue diesel powertrains.
“The shift to 100 per cent full hybrid production for our petrol Mondeo line-up is another big step forward on Ford’s electrification journey,” said Roelant de Waard, vice president, Marketing, Sales & Service, Ford of Europe. “For customers driving less than 20,000 km per year our Mondeo Hybrid is a smart choice, offering an even better deal than diesel, and electric power with no charging or range anxiety.”
One foot in the future
The Mondeo Hybrid combines a specially-developed, Atkinson-cycle 2.0-litre petrol engine, electric motor, generator and 1.4 kWh lithium-ion battery to deliver the driving range and freedom offered by a traditional combustion engine alongside the efficiency and refinement of an electric powertrain.
Regenerative braking technology captures up to 90 per cent of the energy normally lost during braking to replenish the vehicle’s battery. Electric power is used to deliver silent key start capability for refinement particularly in city and stop-start driving scenarios, and to support the petrol engine for optimised fuel efficiency and CO2 emissions.
A Ford-developed power-split automatic transmission seamlessly adjusts for the most efficient use of the powertrain's torque – delivering smooth, linear response to acceleration demand for a refined driving experience.
A SmartGauge interface for monitoring fuel and energy consumption also features Brake Coach, which encourages driving styles that help return more energy to the battery – techniques that will also benefit drivers transitioning to all-electric vehicles in the future.
The Mondeo Hybrid is produced at Ford’s state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in Valencia, Spain – where Ford will also produce full hybrid variants of the S-MAX and Galaxy models from early next year.
Ford is introducing 17 new electrified vehicles to Europe by the end of 2021, and anticipates electrified vehicles will account for more than 50 per cent of all the company’s car sales in Europe by the end of 2022 – surpassing combined sales of conventional petrol and diesel models.
# # #
· Mondeo Hybrid four-door fuel efficiency from 4.1 l/100 km, CO2 emissions from 94 g/km NEDC (5.5 l/100 km, 126 g/km WLTP)
· Mondeo Hybrid wagon fuel efficiency from 4.3 l/100 km, CO2 emissions from 99 g/km NEDC (5.6 l/100 km, 129 g/km WLTP)
· Mondeo 150 PS 2.0-litre EcoBlue four-door fuel efficiency from 4.4 l/100 km, CO2 emissions from 116 g/km NEDC (5.0 l/100 km, 130 g/km WLTP)
· Mondeo 150 PS 2.0-litre EcoBlue wagon fuel efficiency from 4.5 l/100 km, CO2 emissions from 119 g/km NEDC (5.1 l/100 km, 133 g/km WLTP)
The declared fuel/energy consumptions, CO2-emissions and electric range are determined according to the technical requirements and specifications of the European Regulations (EC) 715/2007 and (EU) 2017/1151 as last amended. Light Duty Vehicle type-approved using the World Harmonised Light Vehicle Test Procedure (WLTP) will have fuel/energy consumption and CO2-emission information for New European Drive Cycle (NEDC) and WLTP. WLTP will fully replace the NEDC latest by the end of the year 2020. The applied standard test procedures enable comparison between different vehicle types and different manufacturers. During NEDC phase-out, WLTP fuel consumption and CO2 emissions are being correlated back to NEDC. There will be some variance to the previous fuel economy and emissions as some elements of the tests have altered, so the same car might have different fuel consumption and CO2 emissions.